MPC-TSS wallets - Next Wave of Digital Asset Security

8 mins
Last Edited: Sep 27, 2023
Share
MPC-TSS wallets - Next Wave of Digital Asset Security
Deep dive into different methods of securing digital assets & delegation of key responsibilities among multiple parties
Web3 Wallets
Key Management
Intermediary
This article delves into the realm of securing digital assets and explores different methods for delegating key responsibilities among multiple parties. And, how innovative solutions like Multi-Party Computation (MPC) and the Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) have paved the way towards secure MPC based TSS wallets, addressing the intricate challenges associated with managing digital assets.
As discussed in the previous blog post , that conventional crypto wallets have a problem , once key is lost, all the assets associated with the wallet is lost. Instead of getting caught up in the idea of making copies of the key, let's think about doing something different !
What If, we share the responsibility of managing the key with multiple parties
This responsibility of distributing the key with multiple parties strengthen the security of private keys by reducing the chances of permanent loss due to misplacement or attacks. Moreover, in situations of urgency, a multi-party key management system has the capability to retrieve lost keys.
Lets look at the evolution of different methods that have been designed to make your digital assets ‘SECURE’ -
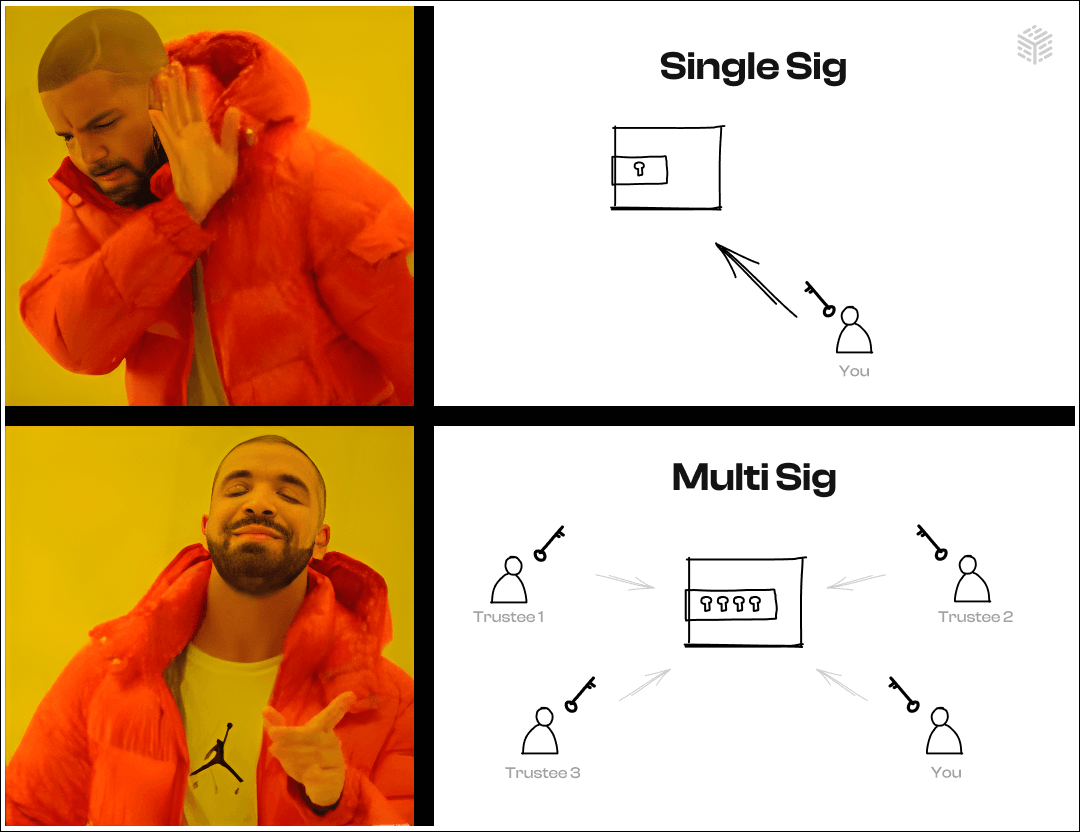
Multi Signature Wallets ( Multi Sigs)
Imagine you have a self custodial wallet that holds your digital assets. Now, instead of just having one lock and one key to open your wallet, multisig sets up multiple locks and keys for this wallet. This means that to access your digital assets, you need a certain number of keys to work together. This sharing of key responsibility adds an extra layer of security to your assets.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| The security of wallet is strengthened- incase even one key is compromised, the entire wallet remains secure. | Multi Signature wallets are not compatible with all the blockchains. |
| It's possible to recover and create backups through trusted parties. | One significant downside of multisig wallets is that their transaction speed is relatively slow because they depend on multiple parties to approve the transactions. |
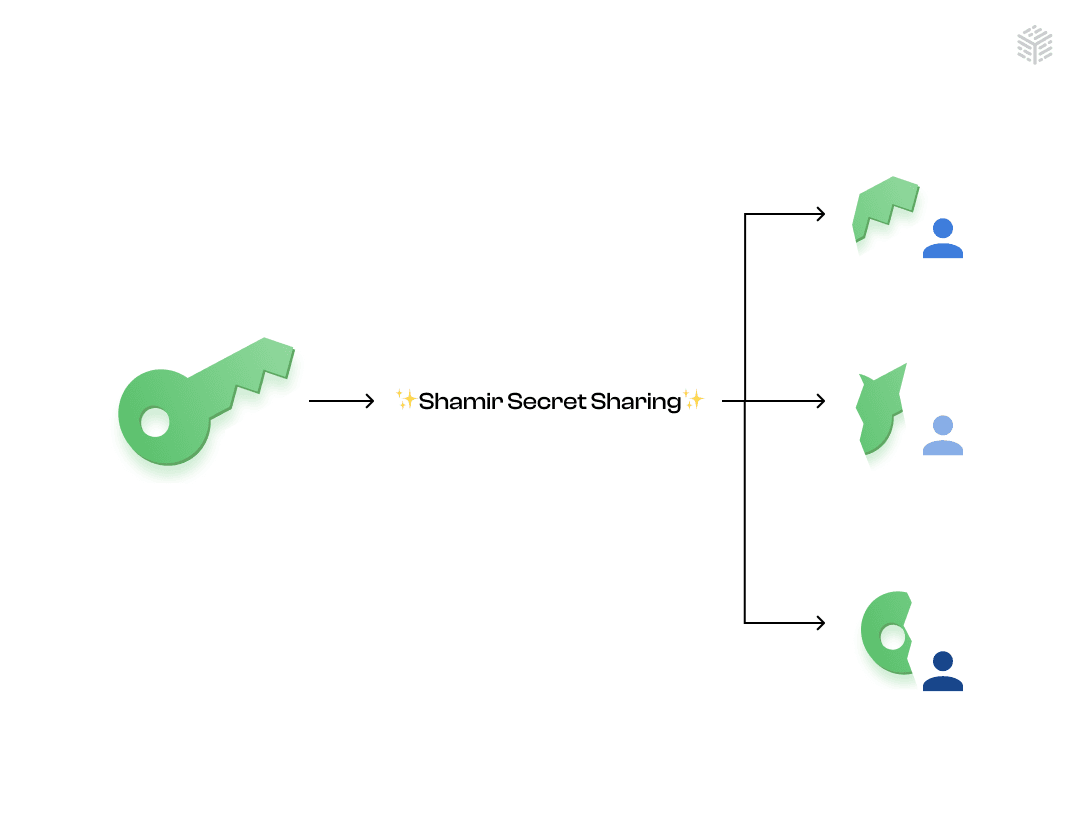
Shamir-Secret Sharing Scheme (SSSS)
It divides the key into multiple parts, or shares, and distributes them among different participants. A predefined number of shares are required to sign the transactions, but any subset of shares(shares=n) is fewer than that threshold value(threshold value = t) , the results aren’t generated. (t<n).
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| It provides a unique advantage in terms of flexibility and extensibility. The algorithm allows the secret owner to adjust the number of shares, add new shares, modify existing shares, or even remove shares without requiring any changes to the original secret. | SSSS has a major drawback: When the key is generated initially or reassembled to unlock the wallet, it is again stored in its original full form. This weakness or storage of keys locally is prone to cyberattacks. |
| SSS supports disaster recovery scenarios. If some shares are lost or compromised, the secret can be reconstructed by gathering the required threshold of shares. This ensures data resilience. | The reconstruction process depends on a stable network connection if shares are distributed across different locations. Network disruptions could impact the process. |
Can we design a system where multiple keys are always kept separate and never combined, while still appearing as a single lock?
This is precisely what Threshold Signatures achieve. These signatures are built on the principles of Multi-Party Computation (MPC) in cryptography. Think of Threshold Signatures as a fusion of the strengths from both Shamir's Secret Sharing Scheme (SSS) and MultiSig.
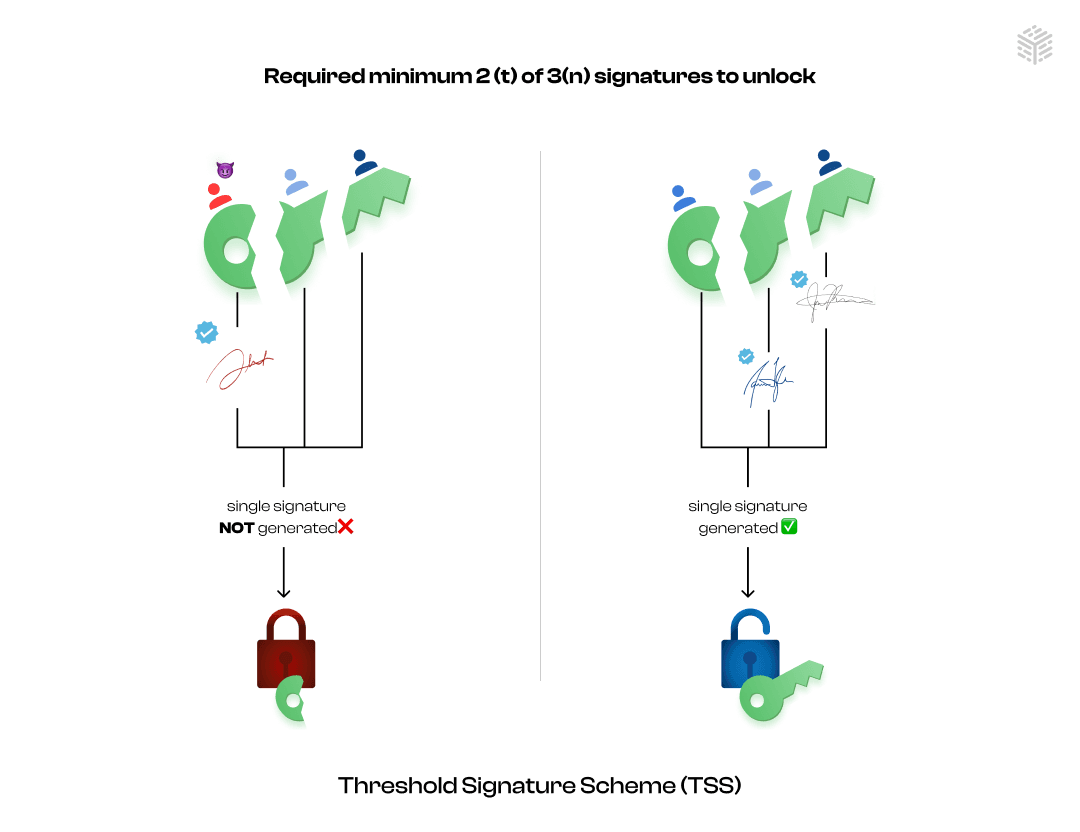
Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS)
At its core, TSS operates by necessitating a selected subset of authorized participants to collaboratively generate digital signatures on behalf of a collective entity. The crux of this mechanism rests upon the concept of a "threshold" value, denoted as 't,' which signifies the minimum number of participants required for the successful generation of a valid signature. Correspondingly, the aggregate number of participants is designated as 'n.' This threshold safeguard ensures that no single participant—whether unintentionally or maliciously—can autonomously execute a signature. Instead, the collective participation of a minimum number of signatories is requisite, thus adding extra layer of security.
In a broader context, the integration of TSS has the potential to profoundly impact the architecture of key management systems in crypto wallets, and pave the way for seamless integration within decentralized finance (DeFi) use cases.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| It is significantly harder for attackers to gain access to a TSS-based crypto wallet, because there is no single point of failure – multiple parties must be compromised in order to get access to the private key. | TSS wallets might have limited compatibility with existing cryptocurrency networks and platforms. Not all blockchains support TSS-based transactions, which could restrict their usage. |
| By involving multiple parties in transaction signing, MPC-based TSS wallets distribute trust. This minimizes reliance on a single trusted entity or third-party, aligning with the decentralized nature of blockchain technology. | TSS are primarily designed for secret sharing and reconstruction, which may not be suitable for all cryptographic applications. Their usage is mainly focused on scenarios where a secret needs to be distributed among multiple parties securely. |
What is Multi- Party Computation ?
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) stands as a cutting-edge cryptographic innovation, offering a secure haven for collaborative computations among multiple participants. This technique help individuals to collectively process functions over their individual private inputs, all while keeping those inputs hidden from each other.
Instead of entrusting sensitive data to a central entity, MPC orchestrates a unique approach: it fragments the data into encrypted fragments, enabling a group of participants to carry out computations on this distributed information without compromising its confidentiality.
MPC is a ‘keyless solution’ since no private keys are shared across the network, only ‘separate’ key shares form the signature.
How Does MPC Work ?
Imagine a scenario where John, Alice, and Charlie want to find out who among them has the highest salary, but they don't want to reveal their actual salary amounts to each other. They decide to use MPC to solve this problem securely.
- Setup: John, Alice, and Charlie agree on a secure MPC protocol and generate cryptographic keys. These keys are used to encrypt and protect their private information.
- Input Sharing: Each person privately shares their salary information using a cryptographic technique called secret sharing. For example, Alice splits her salary into two parts: one encrypted share goes to John, and another encrypted share goes to Charlie. John and Charlie do the same with their salaries, sharing encrypted pieces with the other participants.
- Computation: Using the encrypted shares they received, John, Charlie, and Alice can jointly perform computations without decrypting the shares. In this case, they compare the encrypted salary shares to determine the highest one.
- Result Extraction: After the computation, the MPC protocol produces an output without revealing any individual's salary. For example, the output could indicate that "Alice” has the highest salary" without disclosing the actual salary values.
In this hypothetical example, MPC allows John, Alice and Charlie to collectively determine the highest salary without exposing their individual salary amounts. Each participant keeps their salary private and only contributes their encrypted share for the computation. Through MPC, they can collaborate on finding the answer while keeping their personal information confidential.
Multi-party computation (MPC) protocols must guarantee two fundamental properties: privacy and accuracy.
Privacy: A robust MPC protocol ensures that the private information held by the participating parties remains concealed and cannot be deduced from the protocol's execution. This means that even if an adversary actively observes the protocol's interactions, they should not gain any knowledge about the individual inputs or any confidential information of the parties involved. Privacy protection is crucial to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive data throughout the computation.
Accuracy: Another critical property of an MPC protocol is accuracy. It ensures that even if a subset of parties collude or deviate from the prescribed instructions during the protocol execution, they cannot manipulate the honest parties to generate incorrect outputs or reveal their confidential information. The protocol should maintain the integrity of the computation, guaranteeing that the final result reflects the agreed-upon rules and inputs provided by the honest parties.
MPC -TSS Wallets
MPC wallets offer a solution to eliminate the vulnerability posed by a single point of failure by implementing a Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS). In this approach, the private key is divided into multiple shares, ensuring that no individual person or machine possesses complete control over the private key. This cryptographic technique is known as Distributed Key Generation (DKG).
In an MPC-based threshold signature scheme, the secret key is split into pieces and these pieces are divided among different participants. When a signature is needed, these pieces work together without actually coming together to create the signature. It's like a puzzle where each piece contributes to making the signature without revealing the whole secret key.
The original private key never appear together.
TSS based wallet has an additional security feature- private key rotation. Private key rotation refers to the process of periodically changing the secret shares that constitute a private key without altering the corresponding public key and blockchain address.
This time-based dimension adds an extra layer of complexity for potential attackers, enhancing the overall security of threshold wallets by making it difficult for attackers to attack/hack.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| TSS-based wallets have an additional security feature that allows private key rotation without updating the public key or blockchain address. | The reliance on multiple parties to sign transactions in MPC-based TSS wallets means a stable network connection is crucial. Delays or network issues can slow down transaction processing compared to some other wallet types. |
| MPC-based TSS wallets simplify the user experience. Users don't have to manage their private keys directly, which can be complex and error-prone. This user-friendliness encourages broader adoption. | The technical complexity of MPC-based TSS wallets and their relatively limited availability might hinder their widespread adoption. |
Which Web3 wallets are using MPC?
Few real life examples of Web3 wallets are listed below-
Fireblocks: It provides a secure digital asset management platform for institutions. They utilize MPC technology to secure private keys across multiple parties. Their platform is designed to enable secure storage, transfer, and issuance of digital assets.
Curv: It is a cloud-based institutional digital asset wallet that employs MPC technology for securing private keys. It supports a wide range of cryptocurrencies and enables secure management of assets without the need for traditional hardware wallets.
ZenGo: It is a mobile cryptocurrency wallet that employs MPC to enhance security and user experience. The wallet aims to simplify the process of managing and transacting cryptocurrencies, while maintaining a high level of security through its MPC-based architecture.
OKX In April 2023, OKX enhanced its decentralized wallet with MPC technology. This wallet is non-custodial, ensuring users have full control over their assets. It supports numerous blockchain standards and is particularly beneficial for active traders who frequently exchange tokens and seek to earn yields. Additionally, the OKX wallet comes with a bridge aggregator that links to more than 200 decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
It is a ‘no-fee’ MPC wallet loaded with comprehensive security features. Available as an MPC app on both iOS and Android platforms, it offers safeguarding through fingerprint ID, facial recognition, and dual-factor authentication. Users can also set up transaction limits and even add whitelisted IP wallet addresses. Thousands of cryptocurrencies are supported, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and BNB.
Conclusion
In summary, MPC wallet development introduces a novel and forward-looking approach to enhance the security of cryptocurrency wallets. It brings about elevated security protocols, guarding against potential breaches, and minimizes the susceptibility to human errors.The implementation process of an MPC wallet involves the careful selection of trusted participants, requisite number of parties necessary for configuration, integrating threshold signatures, and opting for a crypto wallet that aligns with compatibility. MPC technology emerges as a dependable avenue for ensuring the secure custody of digital assets.
🔑 Key Takeaway
With these innovative technologies MPC and TSS, the era of irreversible losses and single points of failure is fading into the past, making way for a secure & user-friendly management of digital assets.